Study Medicine Abroad in Europe
Discover how to Study Medicine Abroad in English and begin your journey to become a Doctor.

Dreaming of becoming a doctor and studying medicine abroad, but concerned about language barriers?
Europe offers a treasure trove of world-class medical education in English, paving the way for aspiring physicians from around the globe. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the application process, financing options, and cultural adjustment, while also highlighting the top English-language medical programs that stand out across the continent.
Why Study Medicine Abroad in Europe?
Studying medicine abroad is an excellent choice for several reasons:
What do you want to Study Abroad?
World-renowned universities and cutting-edge research facilities for studying medicine abroad.
Top 10 English-Language Medical Programs Abroad in Europe
Here’s a look at the top English-language medical programs for studying medicine in English abroad across Europe:
University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, UK
- Key Features: Six-year program, early patient contact, cutting-edge research facilities.
Karolinska Institute, Sweden
- Key Features: Five-and-a-half-year program, problem-based learning, opportunities for international exchanges.
Heidelberg University Faculty of Medicine, Germany
- Key Features: Six-year program, integrated practical training, interdisciplinary research focus.
University College London Medical School, UK
- Key Features: Six-year program, emphasis on evidence-based medicine, opportunities for intercalated BSc degrees.
Charles University First Faculty of Medicine, Czech Republic
- Key Features: Six-year program, focus on practical skills, affordable tuition.
University of Zagreb School of Medicine, Croatia
- Key Features: Six-year program, emphasis on research and innovation, beautiful coastal location.
Semmelweis University, Hungary
- Key Features: Six-year program, early clinical exposure, modern approach with affordable tuition.
Trinity College Dublin School of Medicine, Ireland
- Key Features: Five-year graduate entry program, emphasis on clinical skills, opportunities for research.
University of Milan Faculty of Medicine, Italy
- Key Features: Six-year program, integration of basic and clinical sciences, rich cultural experience.
Jagiellonian University Medical College, Poland
- Key Features: Six-year program, problem-based learning, affordable tuition.
Application Requirements and Processes to Study Medicine Abroad
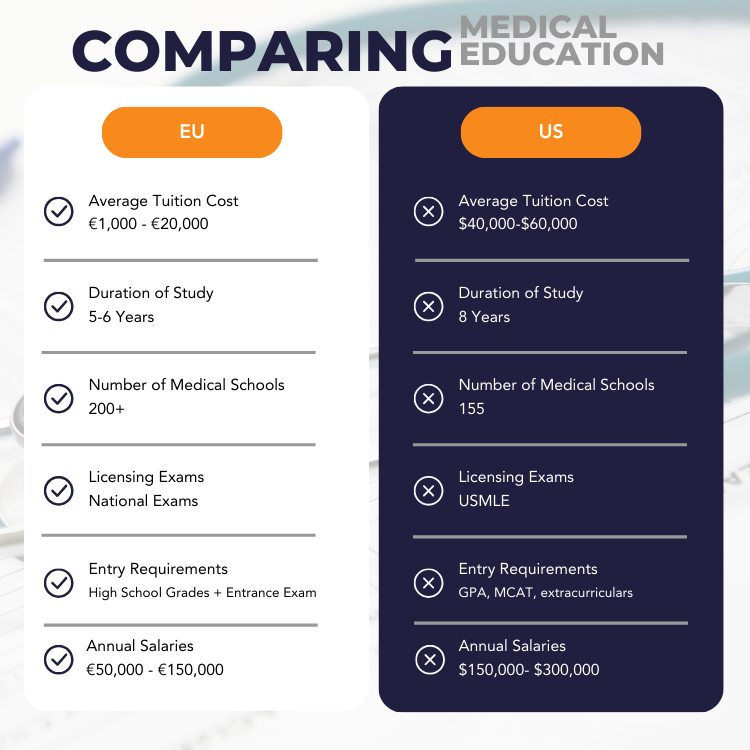
To study medicine abroad in Europe is a promising option for many aspiring medical professionals due to the high quality of education and international recognition of European medical degrees. The application requirements and process vary by country, but there are some common elements.
Applicants typically need a high school diploma or equivalent, with strong grades in science subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics. Proficiency in the language of instruction is also essential; some programs are offered in English, while others require proficiency in the local language. Standardized tests, such as the International Baccalaureate (IB) or A-levels, are often required, and some countries may have their own entrance exams.
The application process generally involves submitting academic transcripts, a personal statement, and letters of recommendation. Many universities also require an entrance examination, such as the UCAT, BMAT, or IMAT, which tests aptitude in areas relevant to medicine. Interviews are also a common part of the selection process.
Furthermore, applicants may need to demonstrate relevant extracurricular activities, such as volunteer work or healthcare-related experiences. Applications are usually submitted through centralized platforms or directly to the universities. Early preparation and understanding specific requirements for each country and institution are crucial for a successful application.
Financing Your Medical Studies Abroad in English
Financing a medical education in Europe involves careful planning and exploring various funding sources, as the costs can vary significantly across countries and institutions. Tuition fees in European medical schools are generally lower than those in the United States, but they can still be substantial, particularly for non-EU students.
Scholarships and grants are a primary source of funding and are offered by universities, governments, and private organizations. These awards can be merit-based, need-based, or specific to certain nationalities or fields of study. Prospective students should research and apply for these opportunities well in advance.
Student loans are another common method of financing education. Some countries offer government-backed loan programs with favorable terms for students, while private loans are also available, though often at higher interest rates. It’s important to understand the repayment conditions and interest rates associated with these loans.
Additionally, many students work part-time while studying to help cover living expenses. However, balancing work and rigorous medical studies can be challenging, so this option should be considered carefully. Some universities offer work-study programs that provide on-campus employment opportunities.
Lastly, family support and personal savings are significant contributors for many students. A combination of these financial resources, along with prudent budgeting and financial planning, can help manage the costs of a medical education in Europe effectively.
Frequently asked questions
Study Medicine Abroad with English Language Programs
- Entry requirements vary by country and university but generally include a high school diploma with strong grades in science subjects, proficiency in the language of instruction, and sometimes entrance exams like the UCAT, BMAT, or IMAT.
- Medical programs in Europe typically last 6 years, including pre-clinical and clinical training.
- Yes, European medical degrees are widely recognized, but it is important to check specific recognition and licensing requirements in your home country.
- While many programs are offered in English, some are in the local language. Proficiency in the language of instruction is essential.
- Tuition fees vary, with EU students often paying lower fees than non-EU students. Additional costs include living expenses, books, and materials.
- Yes, numerous scholarships and financial aid options are available through universities, governments, and private organizations.
- Applications are typically submitted through centralized platforms or directly to universities, requiring academic transcripts, personal statements, and sometimes entrance exams and interviews.
Why Studying Medicine in Europe in English is an Excellent Choice
Studying Medicine in Abroad in English is an excellent choice due to its high-quality education, diverse cultural experiences, and internationally recognized degrees. European medical schools offer rigorous academic programs with a strong emphasis on practical training, preparing students for successful medical careers.
The relatively lower tuition fees, compared to other regions, make it an attractive option financially. Additionally, the opportunity to immerse in different cultures, learn new languages, and engage with a global community enriches the overall student experience.
Graduating with a European medical degree opens doors to numerous career opportunities worldwide, making it a smart and rewarding choice for aspiring medical professionals.

About
The journey to creating Studying Medicine began with my own aspirations of becoming a doctor. When I first decided to pursue a medical degree, I encountered a significant challenge: finding accurate, comprehensive information about studying medicine in Europe. Despite extensive searching, I couldn’t find a single resource that met all my needs. This frustration sparked an idea – if I was struggling to find reliable information, surely others were too. And thus, Studying Medicine was born.

